What is Melanin?
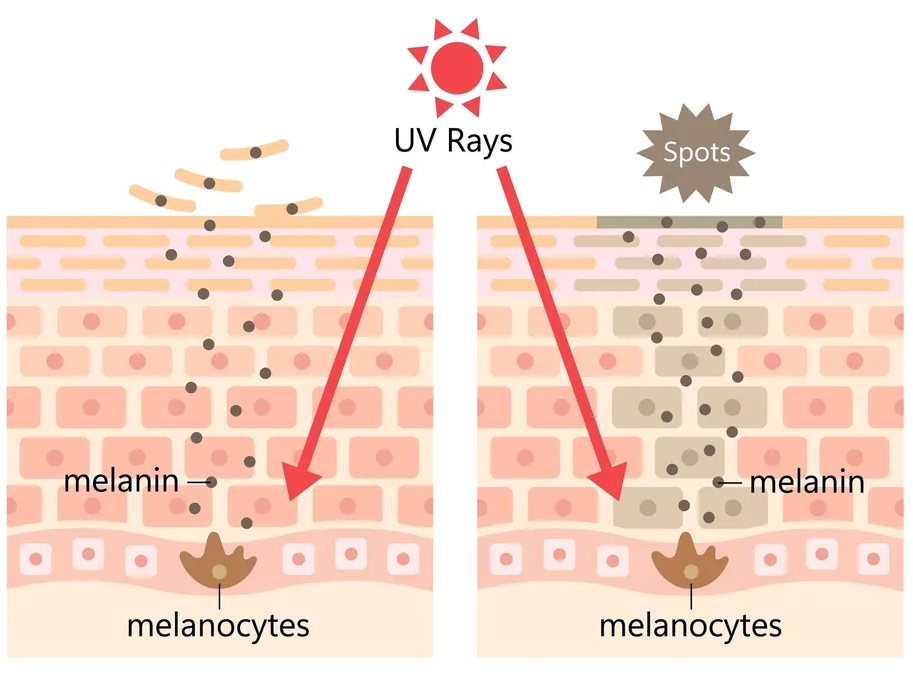
Melanin is a natural pigment found in a variety of organisms. In humans, melanin is primarily responsible for determining the color of the skin, hair, and eyes. Melanin is produced by melanocytes, specialized cells found in the basal layer of the skin’s epidermis.
Melanin serves several important functions in the body:
- Protection from UV Radiation: Melanin helps to absorb and dissipate ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun, thereby protecting the skin from damage that can lead to sunburn, premature aging, and skin cancer.
- Skin Color Determination: The amount and type of melanin produced by melanocytes determine a person’s skin color. Higher levels of melanin result in darker skin tones, while lower levels result in lighter skin tones.
- Eye and Hair Color: Melanin also contributes to the color of the eyes and hair. The type and amount of melanin present in these tissues influence their coloration.
There are two main types of melanin produced in humans:
- Eumelanin: This type of melanin is brown-black in color and is responsible for the majority of skin, hair, and eye pigmentation in humans. It provides protection against UV radiation and is more prevalent in individuals with darker skin and hair.
- Pheomelanin: Pheomelanin is a lighter, reddish-yellow pigment found in smaller quantities compared to eumelanin. It contributes to the red and yellow tones in hair and skin and offers less protection against UV radiation.
The production of melanin is influenced by genetics, hormones, and environmental factors such as sun exposure. Disorders affecting melanin production can lead to conditions like albinism (reduced or absent melanin production) or hyperpigmentation (excessive melanin production), among many others conditions.